2006年NPR美国国家公共电台五月-Study Finds English Are Healthier than Am
时间:2019-01-08 作者:英语课 分类:2006年NPR美国国家公共电台
英语课
Renee Montagne: This is Morning Edition from NPR News, I'm Renee Montagne.
John Ydstie: And I'm John Ydstie. A new study in the Journal of the America Medical Association comes to a conclusion that has surprised even the researchers who conducted it. Middle-aged 1 whites in England are significantly healthier than middle-aged whites in the United States. And that's despite the fact that the US spends twice as much per person on health care. NPR's Joanne Silberner has more.
Joanne Silberner: The researchers from England and the US were just trying to figure out why exactly it is that poor people are less healthy than rich people. They looked at health data from thousands of people in England and the US, all of them 55 to 64 years old and white. They only looked at whites so they could see the effect of socioeconomic status without respect to race. Michael Marmot of University College London said the results they came up with hit him and the other researchers right between the eyes.
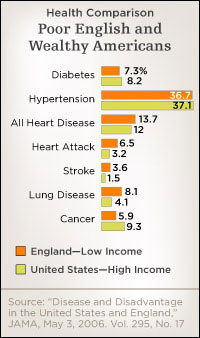
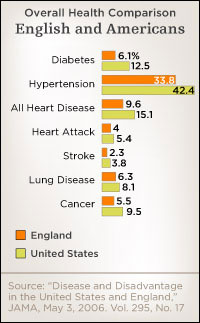
Michael Marmot: Americans have more diabetes 2. Americans have more heart disease. Americans have more respiratory disease and other diseases as well.
Joanne Silberner: That's twice as much diabetes in the US, nearly twice as many people reported cancer.
Michael Marmot: It was a bit of a big shock. I just didn't imagine that we'd find it consistently across the board, with worse health in the US compared with England."
Joanne Silberner: In several categories: diabetes, blood pressure, and cancer, the poorest Brits, those with the lowest third of income levels, did better than the richest third of Americans. The American on the study, economist 3 Jim Smith of the Rand Corporation said Marmot and his colleagues at first didn't believe the data.
Jim Smith: The first reaction I got from my co-authors was that the reason for this must be that American say yes to everything, and so when they're asked whether they're sick or not, they'll say 'Yes.' And I said 'No. I don't think so.' And so when we went into biological markers where it's not just what people say, but we can diagnose the disease ourselves and we find the same thing. It's a real difference and it's huge.
Joanne Silberner: But why? Smith says everyone on the research team has a favorite hypothesis.
Jim Smith: I would emphasize the importance of childhood health conditions. Michael would emphasize the importance of stress, especially stress in, in the workplace, and James Banks would emphasize the obesity 4 epidemic 5. So we all have a different emphasis on what we think the winner might be, but we all agree on what it is not.
Joanne Silberner: It's not the different health systems. The US with higher expenditures 6 and greater availability of technology should score better, not worse. It's not smoking. Rates are about the same in the US and England. And the American obesity epidemic only explains some of the discrepancy 7. Whites in England are getting fatter. But they may have been thinner than their American counterparts as kids. These researchers are doing a new study on what is causing the difference. Some researchers have suggested that a factor called social isolation 8 is at play. Social epidemiologist Lisa Berkman of Harvard University:
Lisa Berkman: We have many, many people working enormous numbers of hours in positions that they feel are insecure, that are, themselves, stressful, but they also have no time to take care of both themselves and their families as well as maintain a certain kind of community neighborhood set of ties.
Joanne Silberner: And what about all those Brits who've moved to the US. Should they worry? Maybe if they've lived here a long time. British researcher Michael Marmot says overtime 9 migrants tend to take on the health patterns of their new countries.
Michael Marmot: The longer they've been in the new country, the more the patterns of health and disease of the new country tend to affect the migrants.
Joanne Silberner: But once you're older and sicker, says American economist Jim Smith, you might as well stay in the US, because Americans spend lots of money to treat diseases of the elderly.
Joanne Silberner: Joanne Silberner, NPR News.
-----------------------
Words in NPR
-----------------------
socioeconomic: based on a combination of social and economic conditions; 社会经济学的
come up with: to think of an idea, answer etc; 赶上, 提出
respiratory disease: disease relating to breathing or your lungs; 呼吸道疾病
epidemiologist: someone who studies the way diseases spread, and how to control them; 流行病学家
-------------------------------------------------------------
John Ydstie: And I'm John Ydstie. A new study in the Journal of the America Medical Association comes to a conclusion that has surprised even the researchers who conducted it. Middle-aged 1 whites in England are significantly healthier than middle-aged whites in the United States. And that's despite the fact that the US spends twice as much per person on health care. NPR's Joanne Silberner has more.
Joanne Silberner: The researchers from England and the US were just trying to figure out why exactly it is that poor people are less healthy than rich people. They looked at health data from thousands of people in England and the US, all of them 55 to 64 years old and white. They only looked at whites so they could see the effect of socioeconomic status without respect to race. Michael Marmot of University College London said the results they came up with hit him and the other researchers right between the eyes.
Michael Marmot: Americans have more diabetes 2. Americans have more heart disease. Americans have more respiratory disease and other diseases as well.
Joanne Silberner: That's twice as much diabetes in the US, nearly twice as many people reported cancer.
Michael Marmot: It was a bit of a big shock. I just didn't imagine that we'd find it consistently across the board, with worse health in the US compared with England."
Joanne Silberner: In several categories: diabetes, blood pressure, and cancer, the poorest Brits, those with the lowest third of income levels, did better than the richest third of Americans. The American on the study, economist 3 Jim Smith of the Rand Corporation said Marmot and his colleagues at first didn't believe the data.
Jim Smith: The first reaction I got from my co-authors was that the reason for this must be that American say yes to everything, and so when they're asked whether they're sick or not, they'll say 'Yes.' And I said 'No. I don't think so.' And so when we went into biological markers where it's not just what people say, but we can diagnose the disease ourselves and we find the same thing. It's a real difference and it's huge.
Joanne Silberner: But why? Smith says everyone on the research team has a favorite hypothesis.
Jim Smith: I would emphasize the importance of childhood health conditions. Michael would emphasize the importance of stress, especially stress in, in the workplace, and James Banks would emphasize the obesity 4 epidemic 5. So we all have a different emphasis on what we think the winner might be, but we all agree on what it is not.
Joanne Silberner: It's not the different health systems. The US with higher expenditures 6 and greater availability of technology should score better, not worse. It's not smoking. Rates are about the same in the US and England. And the American obesity epidemic only explains some of the discrepancy 7. Whites in England are getting fatter. But they may have been thinner than their American counterparts as kids. These researchers are doing a new study on what is causing the difference. Some researchers have suggested that a factor called social isolation 8 is at play. Social epidemiologist Lisa Berkman of Harvard University:
Lisa Berkman: We have many, many people working enormous numbers of hours in positions that they feel are insecure, that are, themselves, stressful, but they also have no time to take care of both themselves and their families as well as maintain a certain kind of community neighborhood set of ties.
Joanne Silberner: And what about all those Brits who've moved to the US. Should they worry? Maybe if they've lived here a long time. British researcher Michael Marmot says overtime 9 migrants tend to take on the health patterns of their new countries.
Michael Marmot: The longer they've been in the new country, the more the patterns of health and disease of the new country tend to affect the migrants.
Joanne Silberner: But once you're older and sicker, says American economist Jim Smith, you might as well stay in the US, because Americans spend lots of money to treat diseases of the elderly.
Joanne Silberner: Joanne Silberner, NPR News.
-----------------------
Words in NPR
-----------------------
socioeconomic: based on a combination of social and economic conditions; 社会经济学的
come up with: to think of an idea, answer etc; 赶上, 提出
respiratory disease: disease relating to breathing or your lungs; 呼吸道疾病
epidemiologist: someone who studies the way diseases spread, and how to control them; 流行病学家
-------------------------------------------------------------


adj.中年的
- I noticed two middle-aged passengers.我注意到两个中年乘客。
- The new skin balm was welcome by middle-aged women.这种新护肤香膏受到了中年妇女的欢迎。
n.糖尿病
- In case of diabetes, physicians advise against the use of sugar.对于糖尿病患者,医生告诫他们不要吃糖。
- Diabetes is caused by a fault in the insulin production of the body.糖尿病是由体內胰岛素分泌失调引起的。
n.经济学家,经济专家,节俭的人
- He cast a professional economist's eyes on the problem.他以经济学行家的眼光审视这个问题。
- He's an economist who thinks he knows all the answers.他是个经济学家,自以为什么都懂。
n.肥胖,肥大
- One effect of overeating may be obesity.吃得过多能导致肥胖。
- Sugar and fat can more easily lead to obesity than some other foods.糖和脂肪比其他食物更容易导致肥胖。
n.流行病;盛行;adj.流行性的,流传极广的
- That kind of epidemic disease has long been stamped out.那种传染病早已绝迹。
- The authorities tried to localise the epidemic.当局试图把流行病限制在局部范围。
n.花费( expenditure的名词复数 );使用;(尤指金钱的)支出额;(精力、时间、材料等的)耗费
- We have overspent.We'll have to let up our expenditures next month. 我们已经超支了,下个月一定得节约开支。 来自《简明英汉词典》
- The pension includes an allowance of fifty pounds for traffic expenditures. 年金中包括50镑交通费补贴。 来自《简明英汉词典》
n.不同;不符;差异;矛盾
- The discrepancy in their ages seemed not to matter.他们之间年龄的差异似乎没有多大关系。
- There was a discrepancy in the two reports of the accident.关于那次事故的两则报道有不一致之处。
n.隔离,孤立,分解,分离
- The millionaire lived in complete isolation from the outside world.这位富翁过着与世隔绝的生活。
- He retired and lived in relative isolation.他退休后,生活比较孤寂。